How to automate and schedule SQL Server index defragmentation
SQL Server maintenance is not a one-time event, but rather a part of a
continuous process. Apart from regular backups and integrity checks,
performance improvements can be achieved with index maintenance. If done
at regular intervals, it can free the server to focus on other requests
rather than losing time scanning for fragmented indexes.
This article should serve as a guide as to how to automate and
schedule SQL Server index defragmentation, and will cover three
different ways of doing it:
- Automate and schedule SQL Server index defragmentation using SQL Server maintenance plans
- Automate and schedule SQL Server index defragmentation using SQL Server Agent jobs
- Automate and schedule SQL Server index defragmentation using ApexSQL Defrag
Automate and schedule SQL Server index defragmentation using maintenance plans
Maintenance plans in SQL Server are a good way to automate some of the
routine tasks. In this section will be explained how to automate and
schedule SQL Server index defragmentation using maintenance plans.
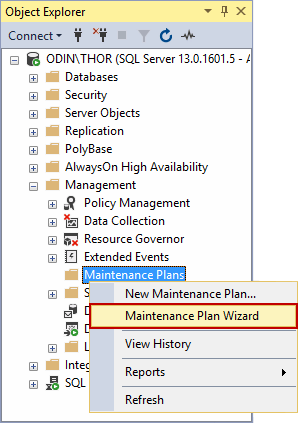
To do that, first we need to open up SQL Server Management Studio.
When SSMS is opened, we need to go to Management and then right-click on Maintenance Plans and select Maintenance Plan Wizard
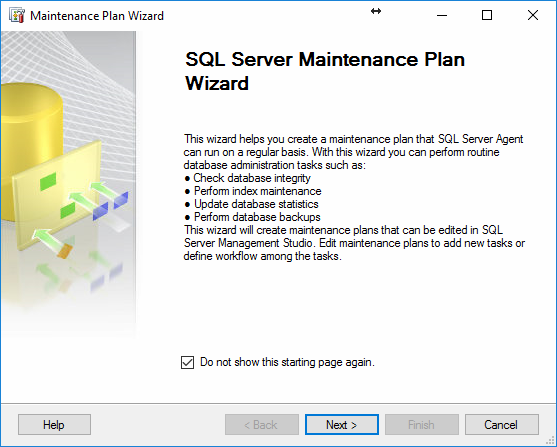
After the wizard opens, go to Next to go to the next page
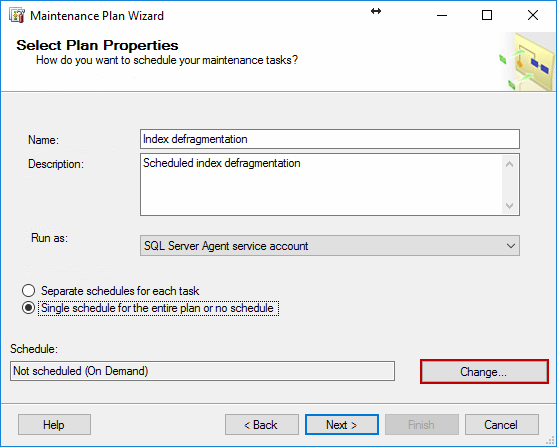
Once there, enter the maintenance plan name, optionally enter the
description, select whether to have a separate schedule for each task or
single schedule for the entire plan or no schedule (for the purposes of
this article, we are going to select the single schedule) and click on Change to edit the schedule
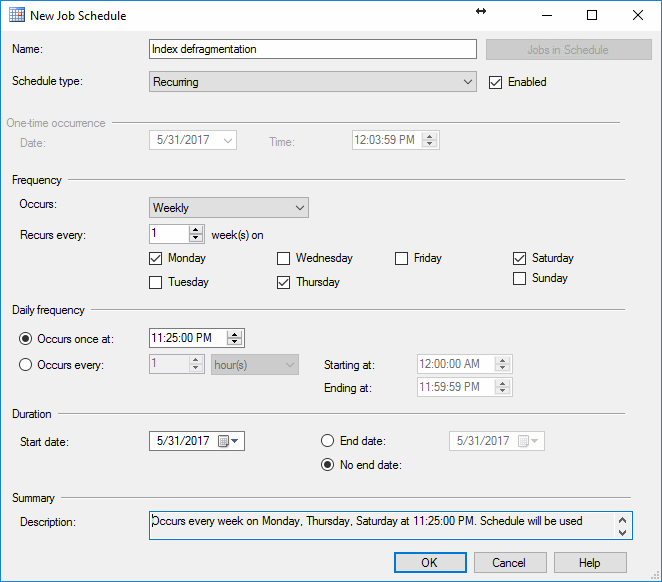
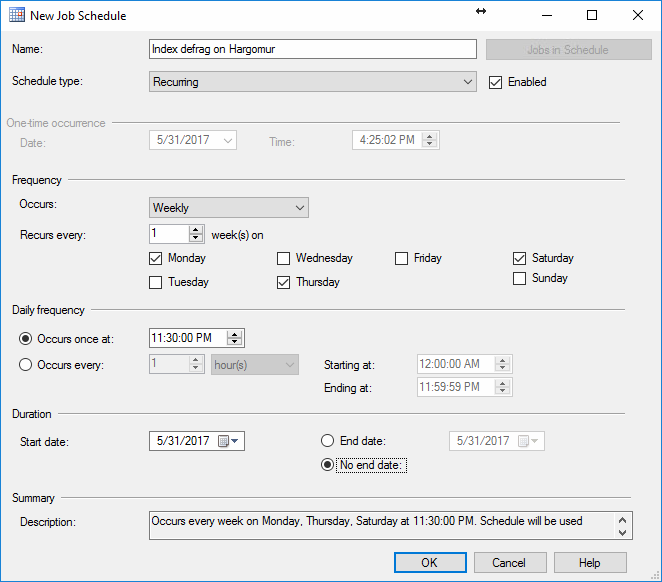
In the New Job Schedule, setup the schedule as per your individual needs.
For the schedule type, there are a few options – Start automatically when SQL Server Agent starts, Start whenever CPUs become idle, Recurring and One time. For the purpose of this article, Recurring is chosen since it allows to schedule precise time when to start the job.
The Frequency option allows choosing whether to do
the job on a daily, weekly or monthly basis. In this case, Weekly is
chosen since it allows to run the job on certain days of the week which
can be beneficial by allowing the user to select the days with the least
amount of traffic on the server.
Daily frequency allows to select a specific time of day to run the job, or a selected time span in which the job runs on an hourly basis.
Duration is used to choose on which day to start the
job and optionally to specify the end date, after which the job will
not run anymore
Moving on to the next page of the wizard, select the maintenance tasks. For the scope of this article, Reorganize Index and Rebuild Index tasks are chosen
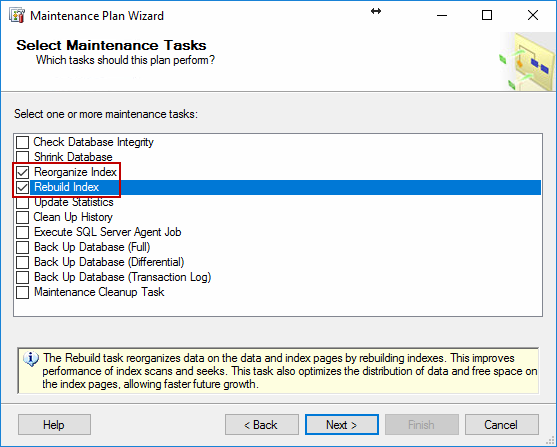
The Select Maintenance Task Order page appears when there’s more than one task chosen. The order is made in this page.
Users can also make a separate maintenance plan for the reorganization
of indexes as well as for the rebuilding of indexes, if needed.
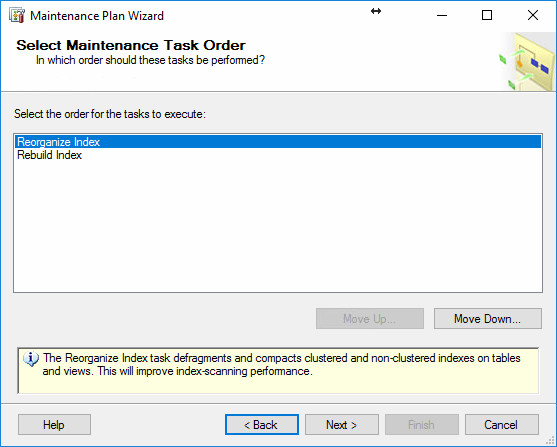
On the next wizard page, Define Reorganize Index Task is where databases can be selected, as well as defining the Scan type and thresholds for the optimization in the Index Stats Options, such as fragmentation percentage, page count and the last time used
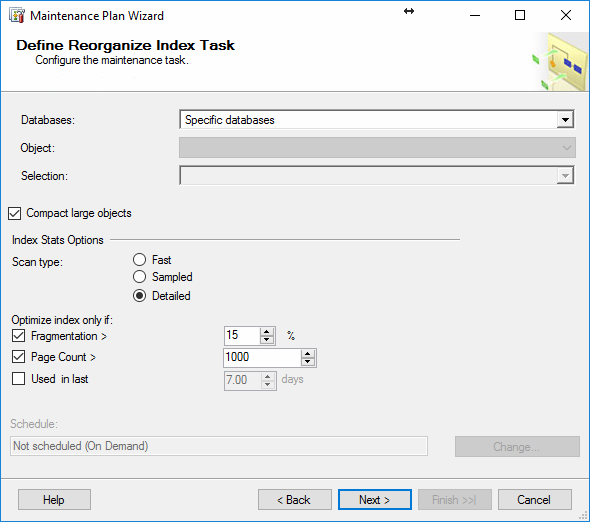
On the following wizard page, Define Rebuild Index Task, databases are selected
Free space options, the free space per page, or Fill factor,
can be left as default values or changed (doing this changes the free
space per page for all the indexes in the selected databases, which in
some cases can be detrimental to the overall performance and
fragmentation, despite the rebuild process)
Advanced options offer different options, such as sorting the results in tempdb, online index rebuild, maximum degree of parallelism among others.
Index Stats Options allows defining the thresholds and scan type
In the next wizard page, Select Report Options, it can be chosen to write a report to a text file, and/or send an email report
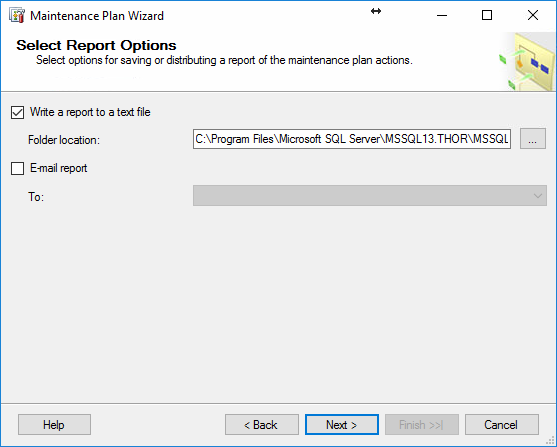
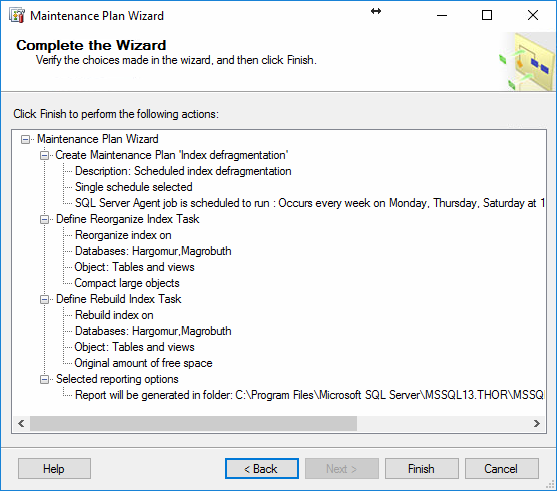
In the final page of the wizard the whole maintenance plan with all
the tasks can be reviewed and created by pressing on the finish button
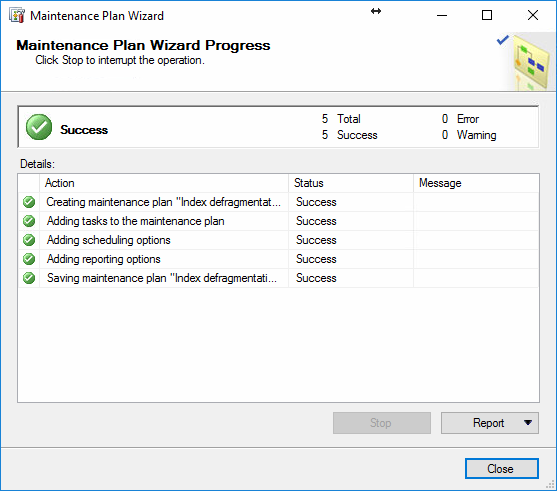
After pressing on the Finish button, the maintenance plan is being
created and is presented at the end of the wizard as a series of
operations, which, if successful, should look like in the image below
Automate and schedule SQL Server index defragmentation using a SQL Server Agent job
As well as maintenance plans, SQL Server Agent jobs are also a handy
way to automate and schedule index defragmentation jobs in SQL Server.
They are also configured from SSMS
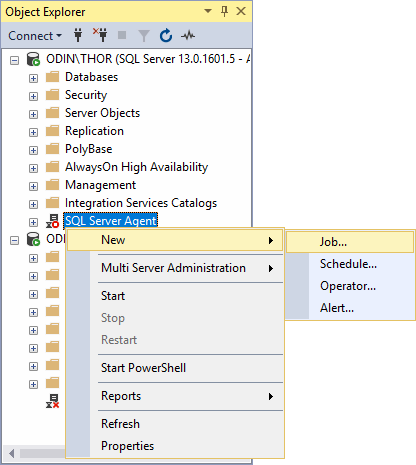
To create a new job, right click on SQL Server Agent, select New and then Job
Next the New Job window will open. In it, enter the Job name, owner, optionally Category and Description
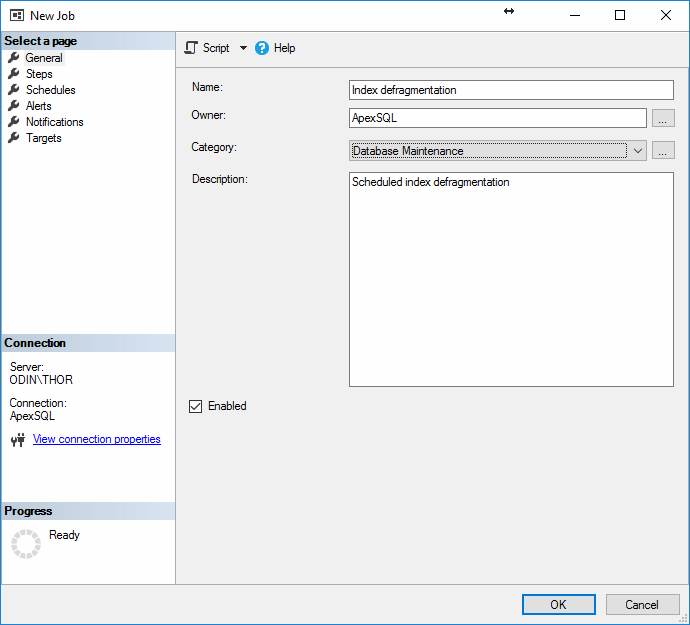
In the next tab, Steps, click on New to open a New Job Step window
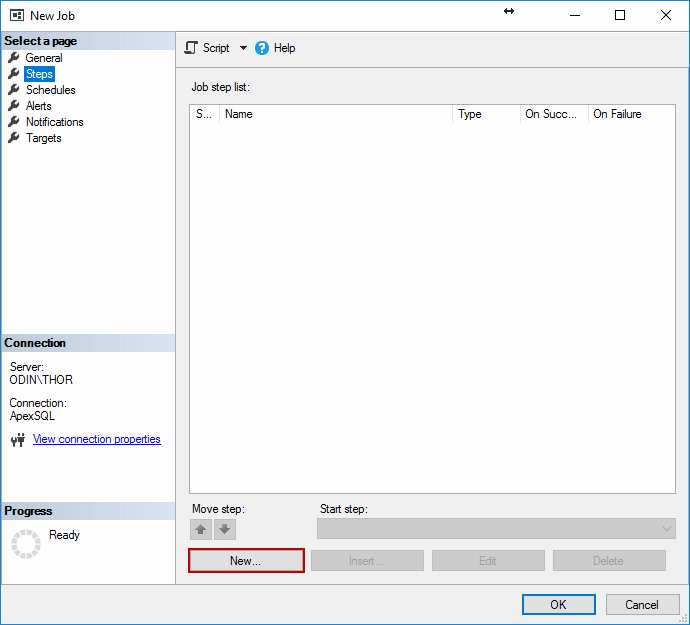
In the New Job Step, insert the Step Name, select the type of step to be Transact-SQL script (T-SQL), select the database to defragment
Note: For SQL Server Agent job steps, only one database can be selected in a single step
In the Command: window, enter the following T-SQL script which was taken and adapted from MSDN Books Online article “Rebuild or reorganize indexes (with configuration)” :
USE <databasename> SET NOCOUNT ON DECLARE @reorg_frag_thresh float SET @reorg_frag_thresh = 10.0 DECLARE @rebuild_frag_thresh float SET @rebuild_frag_thresh = 30.0 DECLARE @fill_factor tinyint SET @fill_factor = 80 DECLARE @report_only bit SET @report_only = 1 -- added (DS) : page_count_thresh is used to check how many pages the current
table uses DECLARE @page_count_thresh smallint SET @page_count_thresh = 1000 -- Variables required for processing. DECLARE @objectid int DECLARE @indexid int DECLARE @partitioncount bigint DECLARE @schemaname nvarchar(130) DECLARE @objectname nvarchar(130) DECLARE @indexname nvarchar(130) DECLARE @partitionnum bigint DECLARE @partitions bigint DECLARE @frag float DECLARE @page_count int DECLARE @command nvarchar(4000) DECLARE @intentions nvarchar(4000) DECLARE @table_var TABLE( objectid int, indexid int, partitionnum int, frag float, page_count int ) -- Conditionally select tables and indexes from the -- sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats function and -- convert object and index IDs to names. INSERT INTO @table_var SELECT [object_id] AS objectid, [index_id] AS indexid, [partition_number] AS partitionnum, [avg_fragmentation_in_percent] AS frag, [page_count] AS page_count FROM sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats (DB_ID(), NULL, NULL , NULL, 'LIMITED') WHERE [avg_fragmentation_in_percent] > @reorg_frag_thresh AND page_count > @page_count_thresh AND index_id > 0 -- Declare the cursor for the list of partitions to be processed. DECLARE partitions CURSOR FOR SELECT * FROM @table_var -- Open the cursor. OPEN partitions -- Loop through the partitions. WHILE (1=1) BEGIN FETCH NEXT FROM partitions INTO @objectid, @indexid, @partitionnum, @frag, @page_count IF @@FETCH_STATUS < 0 BREAK SELECT @objectname = QUOTENAME(o.[name]), @schemaname = QUOTENAME(s.[name]) FROM sys.objects AS o WITH (NOLOCK) JOIN sys.schemas as s WITH (NOLOCK) ON s.[schema_id] = o.[schema_id] WHERE o.[object_id] = @objectid SELECT @indexname = QUOTENAME([name]) FROM sys.indexes WITH (NOLOCK) WHERE [object_id] = @objectid AND [index_id] = @indexid SELECT @partitioncount = count (*) FROM sys.partitions WITH (NOLOCK) WHERE [object_id] = @objectid AND [index_id] = @indexid -- Build the required statement dynamically based on options and index
stats. SET @intentions = @schemaname + N'.' + @objectname + N'.' + @indexname + N':' + CHAR(13) + CHAR(10) SET @intentions = REPLACE(SPACE(LEN(@intentions)), ' ', '=') + CHAR(13) + CHAR(10) + @intentions SET @intentions = @intentions + N' FRAGMENTATION: ' + CAST(@frag AS nvarchar) + N'%' + CHAR(13) +CHAR(10) + N' PAGE COUNT: ' + CAST(@page_count AS nvarchar) + CHAR(13) +CHAR(10) IF @frag < @rebuild_frag_thresh BEGIN SET @intentions = @intentions + N' OPERATION: REORGANIZE' + CHAR(13) + CHAR(10) SET @command = N'ALTER INDEX ' + @indexname + N' ON ' + @schemaname + N'.' + @objectname + N' REORGANIZE; ' + N' UPDATE STATISTICS ' + @schemaname + N'.' + @objectname + N' ' + @indexname + ';' END IF @frag >= @rebuild_frag_thresh BEGIN SET @intentions = @intentions + N' OPERATION: REBUILD' + CHAR(13) + CHAR(10) SET @command = N'ALTER INDEX ' + @indexname + N' ON ' + @schemaname + N'.' + @objectname + N' REBUILD' END IF @partitioncount > 1 BEGIN SET @intentions = @intentions + N' PARTITION: ' + CAST(@partitionnum AS nvarchar(10)) + CHAR(13) +CHAR(10) SET @command = @command + N' PARTITION=' + CAST(@partitionnum AS nvarchar(10)) END IF @frag >= @rebuild_frag_thresh AND @fill_factor > 0 AND @fill_factor < 100 BEGIN SET @intentions = @intentions + N' FILL FACTOR: ' + CAST(@fill_factor AS nvarchar) + CHAR(13) + CHAR(10) SET @command = @command + N' WITH (FILLFACTOR = ' + CAST(@fill_factor AS nvarchar) + ')' END -- Execute determined operation, or report intentions IF @report_only = 0 BEGIN SET @intentions = @intentions + N' EXECUTING: ' + @command PRINT @intentions EXEC (@command) END ELSE BEGIN PRINT @intentions END PRINT @command END -- Close and deallocate the cursor. CLOSE partitions DEALLOCATE partitions GO
Note: Make sure to enter the database name in the
first line of the script according to the environment in which the job
will be used
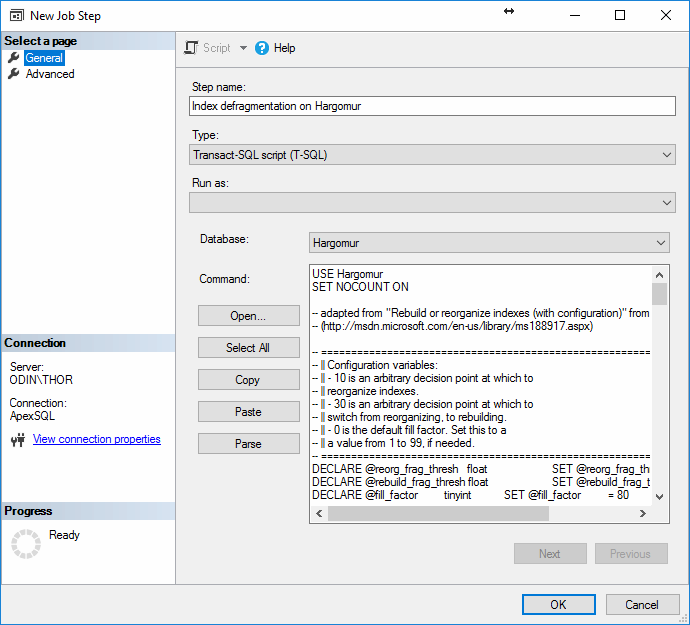
In the advanced tab of the same window, action on success, action on
failure can be set from the dropdown menus, as well as the ability to
export the script to a file, log the action to table and include the
step output in history
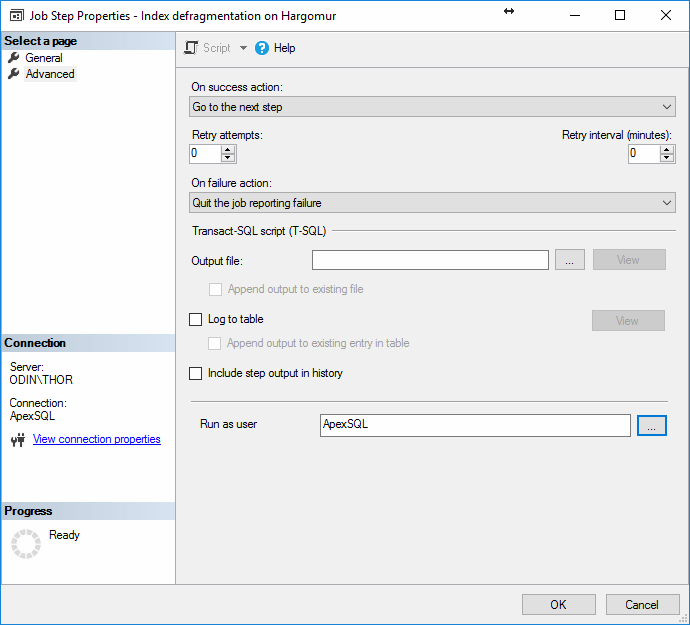
After creating the step, the New Job window should look something like this
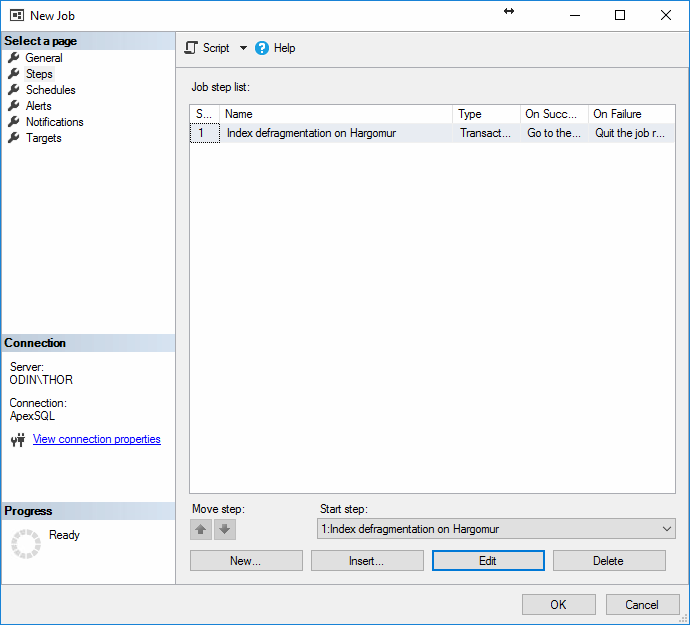
On the next tab, Schedules, click on New… to open the New Job Schedule
In the New Job Schedule, same as when creating the schedule for maintenance plans, a detailed schedule can be set up
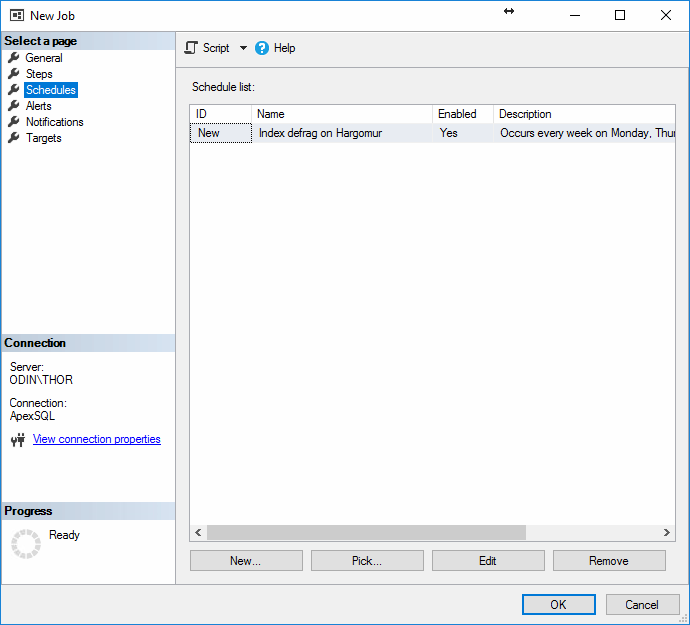
After creating the schedule, the New Job window should look as follows
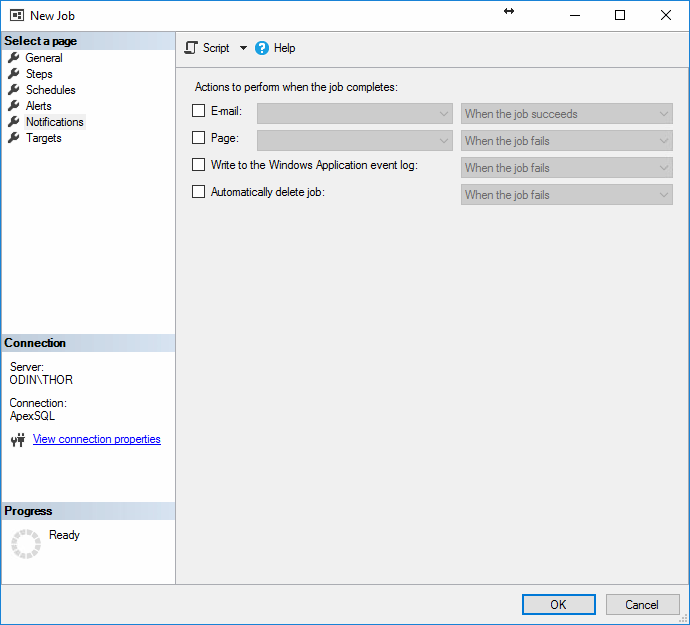
On the Alerts tab, alerts can be setup in case of specific events
On the Notifications tab, email notifications, pager
messages can be sent, an entry in the Windows Application event log can
be made and the job can be deleted automatically upon success or failure
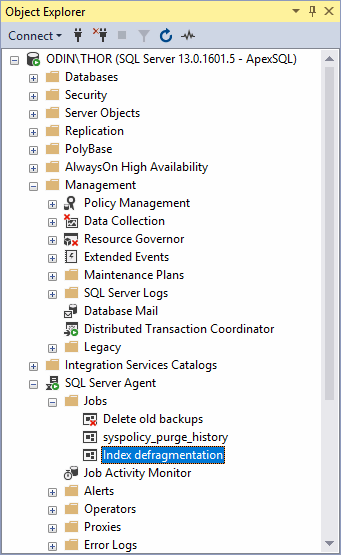
After pressing OK, the job will be created, and can afterwards be viewed in the Object Explorer under the SQL Server Agent – Jobs
Related Articles
ePolicy Orchestrator clean installation or upgrade fails when using either of the SQL options AlwaysOn or SQL mirroring
Environment McAfee ePolicy Orchestrator (ePO) 5.x Microsoft SQL Server Problem ePO upgrades or a fresh installation fail on servers that use either of the following SQL options: AlwaysOn SQL mirroring The following error displays after you enter the ...ePolicy Orchestrator cannot make outbound connections to SQL, LDAP, or other servers where TLS 1.0 is disabled
Environment McAfee ePolicy Orchestrator (ePO) 5.10 Summary Starting with ePO 5.10, the protocol Transport Layer Security (TLS) 1.0 is disabled by default. Any outbound connections from ePO to another external system must support TLS 1.1 or higher. ...McAfee ePolicy Orchestrator server backup and disaster recovery procedure
Environment McAfee ePolicy Orchestrator (ePO) 5.x Summary This article provides information about the backup and disaster recovery process for the ePO server. IMPORTANT: This procedure is intended for use by network and ePO administrators only. ...ePolicy Orchestrator server backup and disaster recovery procedure (Technical Articles ID:KB66616)
Environment McAfee ePolicy Orchestrator (ePO) 5.x Summary This article provides information on the backup and disaster recovery process for ePO servers. IMPORTANT: This procedure is intended for use by network and ePO administrators only. McAfee ...ePolicy Orchestrator 5.1 or 5.3 server tasks do not expire after reaching abort time
Environment McAfee ePolicy Orchestrator (ePO) 5.3.0, 5.1.1, or 5.1.0 Problem If ePO is unable to connect to a client system, certain server tasks (including Agent Wakeup Call, Agent Deployment, and AD sync) may remain in an In Progress state ...